Python/알면 쓸모있는 잡다한 코드
Dictionary within Dictionary 이중 딕셔너리
joannekim0420
2021. 11. 25. 12:36
728x90
상황: 11개 폴더 안에 200~300개의 여러 파일들이 있는데 (각 폴더 안에 파일도 같은 이름으로 있을 수도 없을 수도)
같은 파일명끼리 그리고 파일 안 같은 라인끼리 추출해야함!
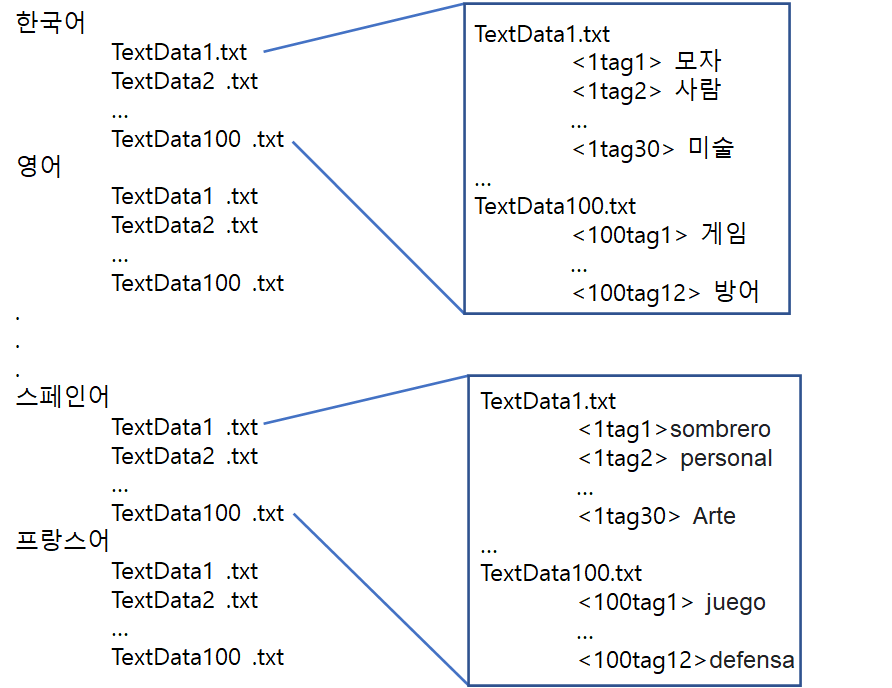
그림과 같이 언어 이름으로 된 폴더 안에 TextData1.txt 같이 파일이 있고 각 파일 안에는 고유 태그 이름과 용어가 있다.
1. 언어별로 같은 파일이름 TextData1, TextData2 ... TextData100 으로 된 파일의 존재 여부를 확인(가끔 언어별로 파일이 없을 수도 있기 때문)
→ 각 파일 이름을 딕셔너리 key 로 value는 해당 언어명을 저장한다!
import collections
file_name_dict= collections.defaultdict(list)
# {'file_name' : ['lang1','lang2'...]}
for lst, l in zip((PT,CHS,CHT,EN,FR,DE,JA,KR,RU,TH,VI),lang):
add_filename_dict(lst,l)
# check if dictionary is in correct form
for key, value in file_name_dict.items():
print(f"{key} {value} ")output

2. 각 파일에 대한 각 라인별 고유 태그와 용어를 저장해야하는데, 이중 딕셔너리와 튜플까지 사용한다.
total_list_dict = collections.defaultdict(list)
def extract_matching_lines_by_tag():
for file_name in file_name_dict.items():
# file_name[0] => key
# file_name[1] => value
# line_name_dict for tag as key and each language and word information
line_name_dict = collections.defaultdict(list)
# Dictionary will be like => {'tag':[(lang,word),(lang,word)...(lang,word)]}
for l in lang:
in_path = "./" + l+"/"+file_name[0]
# Files only in that language folder
if l in file_name[1]:
# some files in utf-8, some files in utf-16
try:
fread = open(in_path, "r",encoding="utf-16")
lines = fread.readlines() #read all lines in one file
except:
fread = open(in_path, "r",encoding="utf-16")
lines = fread.readlines()
# for each line in all lines
for line in lines:
line = line.strip()
line = re.sub("\n","",line)
unique_tag_pattern = "<tag_.+?\">"
#find unique tag in each line and save the tag name
tag = re.findall(unique_tag_pattern, line)
#extract only the word necessary and remove all unnecessary tags
line_in_need = re.sub("<.+?>","",line)
line_in_need = line_in_need.strip()
#if there is no tag in line
if bool(tag) == False:
continue
else:
for t in tag:
# only add if there is word you want
if line_in_need != "":
# value must be (lang, word) tuple form - need info on what word that language is
line_name_dict[t].append((l,line_in_need))
# if one file is done on all language add the dictionary to another dictionary
# double dictionary form {{'file name' : {'unique_tag_name' : [(lang,word)],[(lang,word)]}}
total_list_dict[file_name[0]].append(line_name_dict)extract_matching_lines_by_tag()
# check if dictionary form is correct
for key, value in total_list_dict.items():
print(f"{key} {value} ")
break
break 로 total_list_dict의 딕셔너리 안에 한 파일만 출력해 보았다. (이유: 모든 파일 다 출력하면 memory error 발생)
이제 이 딕셔너리 속 정보는 알아서 활용!
나는 파일별로 저장하는게 목표
for key,value in total_list_dict.items():
out_path = "./RESULT/"+key
fwrite = open(out_path,"w",encoding="utf-8")
# line_name_dict 와 같음. 라인별 (언어,용어) 접근 위해 딕셔너리 따로 value_dict로 저장
value_dict = value[0]
# k = unique_tag_name , v = (lang,word) pair list
for k,v in value_dict.items():
v_list = {}
# save needed languages in line
for i in range(len(v)):
v_list[v[i][0]] = v[i][1]
# if language is in each line
for l in lang:
if l in v_list:
if l == "Portuguese" :
fwrite.write(v_list[l]+"\t")
elif l == "Chinese" :
fwrite.write(v_list[l]+"\t")
elif l == "English" :
fwrite.write(v_list[l]+"\t")
elif l == "French" :
fwrite.write(v_list[l]+"\t")
## add all language
elif l == "Vietnamese":
fwrite.write(v_list[l]+"\n") #last lanugage, seperate by line
# if language does not exist in line fill it with blank
else:
if l == "Vietnamese":
fwrite.write("\t\n")
else:
fwrite.write("\t")
# save by file name
fwrite.close()